public interface Counter {
long incAndGet();
long get();
}Concurrency
thread synchronization
Problem
Example
public class CounterSimple implements Counter {
private long count = 0;
public void increment() {
count++;
}
public long get() {
return count;
}
}Example
public static void main(String[] args) {
Counter sharedCounter = new CounterSimple();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(getRunnable(sharedCounter, "Tread-1 final count:"));
Thread thread2 = new Thread(getRunnable(sharedCounter, "Tread-2 final count:"));
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
private static Runnable getRunnable(Counter counter, String message) {
return () -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 1_000_000; i++) {
counter.increment();
}
System.out.printf("%s %d\n", message, counter.get());
};
}Example
Tread-2 final count: 1011580 Tread-1 final count: 1877091
Why?
public class CounterDetail implements Counter {
private long count = 0;
public void increment() {
long tmp = count; // read
tmp = tmp + 1; // modify
count = tmp; // write
}
public long get() {
return count;
}
}Problem
Data Race
OR
Read, Modify, Write problem
Definition
Data Race - это состояние когда разные потоки обращаются к одной ячейке памяти
без какой-либо синхронизации
и как минимум один из потоков осуществляет запись.
Example
private static Runnable getRunnable(Map<String, String> sharedMap, String value) {
return () -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 1_000_000; i++) {
if (sharedMap.containsKey("switcher")) {
String currentValue = sharedMap.remove("switcher");
if (currentValue == null) {
System.out.printf("%s, iteration %d\n", value, i);
}
} else {
sharedMap.put("switcher", value);
}
}
System.out.println();
};
}Example
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> sharedMap = new HashMap<>();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(getRunnable(sharedMap, "Tread-1"));
Thread thread2 = new Thread(getRunnable(sharedMap, "Tread-2"));
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}Example
Tread-1, iteration 699274 Tread-2, iteration 997524 Tread-2, iteration 997527 Tread-1, iteration 701708 Tread-1, iteration 701723
Why?
if (sharedMap.containsKey("switcher")) { // check
String currentValue = sharedMap.remove("switcher"); // then act
if (currentValue == null) {
System.out.printf("%s, iteration %d\n", value, i);
}
} else {
sharedMap.put("switcher", value);
}Problem
Race Condition
OR
Check Then Act problem
Definition
Race Condition — это недостаток, возникающий, когда время или порядок событий влияют на правильность программы.
Race condition — это семантическая ошибка.
Нет общего способа который может отличить правильное и неправильное поведение программы в общем случае.
Concurrency: Thread Synchronization
Types of thread synchronization
Mutual Exclusive (взаимное исключение)
synchronized method
synchronized block
static synchronization
Cooperation (Inter-thread communication in java) (кооперация)
Mutual Exclusive
Для устранения некоторых проблем в многопоточности, используют блокировки с помощью объекта.
Любой объект может быть заблокирован.
Снятие блокировки производится автоматически.
Monitor
Монитор – это объект, который используется для взаимоисключающей блокировки (mutually exclusive lock) - mutex.
Любой объект может быть монитором.
Для взаимодействия с монитором поток должен иметь блокировку на него.
Operator synchronized
synchronized block
class CountThread implements Runnable {
private final CommonResource res;
public CountThread(CommonResource res) {
this.res = res;
}
public void run() {
synchronized (res) {
res.x = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
System.out.printf("%s %d \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), res.x);
res.x++;
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}synchronized method
class CommonResource {
private int x;
synchronized void increment() {
x = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
System.out.printf("%s %d \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), x);
x++;
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}synchronized method
class CountThread implements Runnable {
private final CommonResource res;
public CountThread(CommonResource res) {
this.res = res;
}
public void run() {
res.increment();
}
}Cooperation
Methods
wait()notify()notifyAll()
Thread Lifecycle
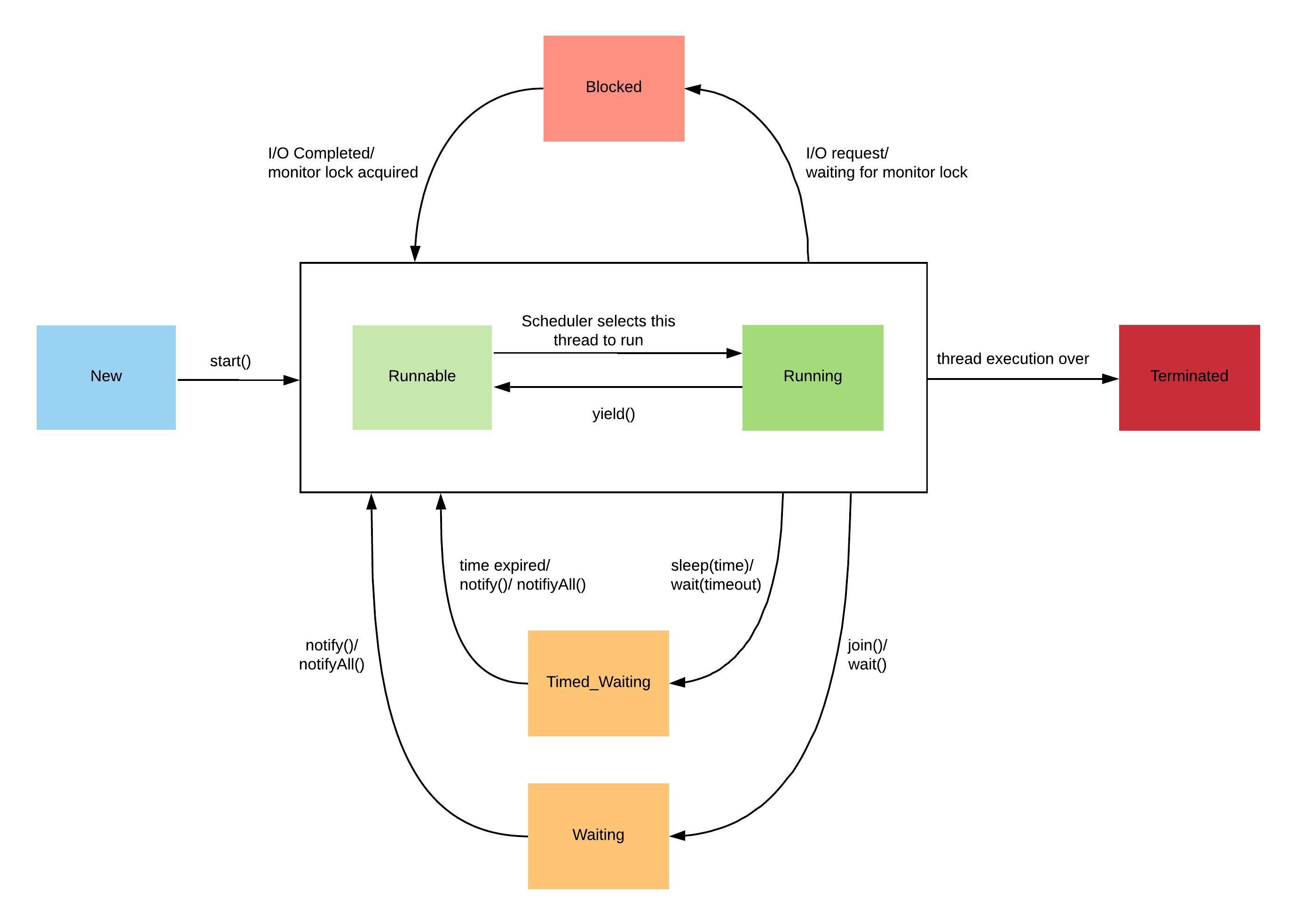
Example
// Класс Магазин, хранящий произведенные товары
public class Store {
private int product = 0;
public synchronized void get() {
while (product < 1) {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
product--;
System.out.println("Покупатель купил 1 товар");
System.out.println("Товаров на складе: " + product);
notify();
}
public synchronized void put() {
while (product >= 3) {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
product++;
System.out.println("Производитель добавил 1 товар");
System.out.println("Товаров на складе: " + product);
notify();
}
}Example
class Producer implements Runnable {
private Store store;
public Producer(Store store) {
this.store = store;
}
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
store.put();
}
}
}Example
class Consumer implements Runnable {
private Store store;
public Consumer(Store store) {
this.store = store;
}
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
store.get();
}
}
}Example
public class Program {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Store store=new Store();
Producer producer = new Producer(store);
Consumer consumer = new Consumer(store);
new Thread(producer).start();
new Thread(consumer).start();
}
}Typical problems in Java concurrency
Deadlock (взаимная блокировка)
Starvation (голодание)
Nested Monitor Lockout (блокировка вложенного монитора)
Slipped Conditions (изменчивое условие)
Deadlock

Deadlock
public class BankAccount {
private final String fullName;
private double balance;
public BankAccount(String fullName, double balance) {
this.fullName = fullName;
this.balance = balance;
}
public synchronized void deposit(double amount) {
balance += amount;
}
public synchronized void withdraw(double amount) {
balance -= amount;
}
public synchronized void transfer(double amount, BankAccount target) {
System.out.printf("%s is using monitor for object with full name: %s.\n",
Thread.currentThread().getName(),
this.getFullName());
withdraw(amount);
try {
Thread.sleep(1_000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.printf("%s want to use monitor for object with full name: %s.\n",
Thread.currentThread().getName(),
target.getFullName());
target.deposit(amount);
}
public String getFullName() {
return fullName;
}
}Deadlock
public class MoneyTransfer implements Runnable {
private final BankAccount from, to;
private final double amount;
public MoneyTransfer(BankAccount from, BankAccount to, double amount) {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.amount = amount;
}
public void run() {
from.transfer(amount, to);
}
}Deadlock
public class ExampleDeadlock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BankAccount aliceAccount =
new BankAccount("Jon Turing", 5000.0);
BankAccount bobAccount =
new BankAccount("Bill Lee", 10000.0);
Runnable transaction1 =
new MoneyTransfer(aliceAccount, bobAccount, 1200);
Thread t1 = new Thread(transaction1);
t1.start();
Runnable transaction2 =
new MoneyTransfer(bobAccount, aliceAccount, 700);
Thread t2 = new Thread(transaction2);
t2.start();
}
}Deadlock
Thread-0 is using monitor for object with full name: Jon Turing. Thread-1 is using monitor for object with full name: Bill Lee. Thread-0 want to use monitor for object with full name: Bill Lee. Thread-1 want to use monitor for object with full name: Jon Turing.
Starvation
