while (booleanExpression) {
// statement(s) (body of loop)
}Looping statements
Intro
Problem
Что если нужно вывести сообщение 100 раз?
Повторим код по выводу 100 раз!
Solution
Вместо того чтобы писать один и тот же код 100 раз, можно использовать цикл.
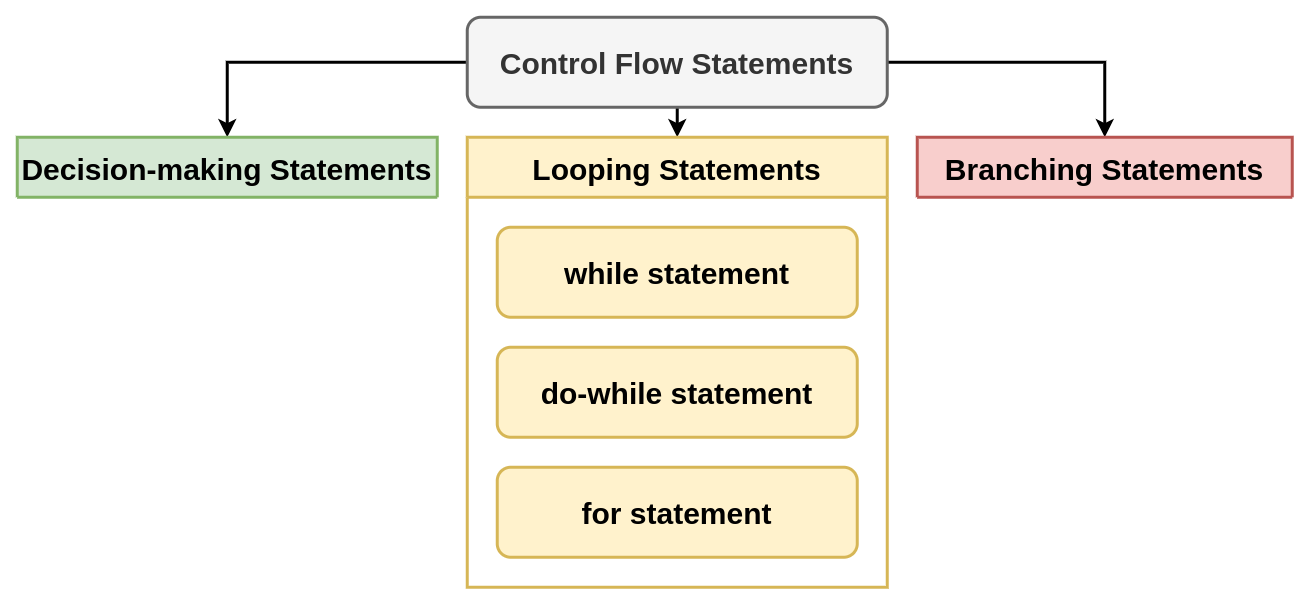
Control Flow Statements
Looping statements
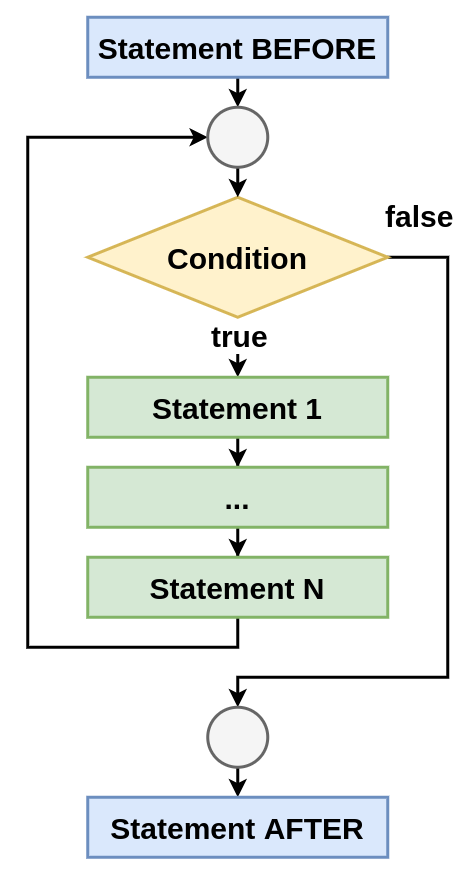
while statement
Block schema
Syntax
Syntax
while (booleanExpression)
// ONE statementDo not recommend
Example
// declare variables
int i = 1;
int n = 5;
// while loop from 1 to 5
while (i <= n) {
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}1
2
3
4
5How this program works?
| Iteration | Variable | i <= n | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
1st |
|
|
|
2nd |
|
|
|
3rd |
|
|
|
4th |
|
|
|
5th |
|
|
|
6th |
|
| The loop is terminated. |
Example
// declare variables
int i = 1;
// infinity while loop
while (true) {
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}1
2
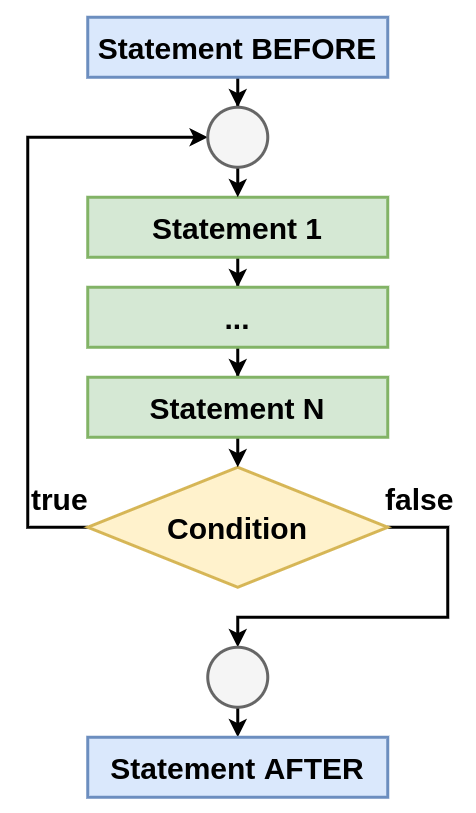
...do-while statement
Block schema
Syntax
do {
// statement(s) (body of loop)
} while (booleanExpression);Syntax
do
// ONE statement
while (booleanExpression);Do not recommend
Example
int i = 1;
int n = 5;
// do-while loop from 1 to 5
do {
System.out.println(i);
i++;
} while (i <= n);1
2
3
4
5Example
int i = 1;
// infinity do-while loop
do {
System.out.println(i);
i++;
} while (true);1
2
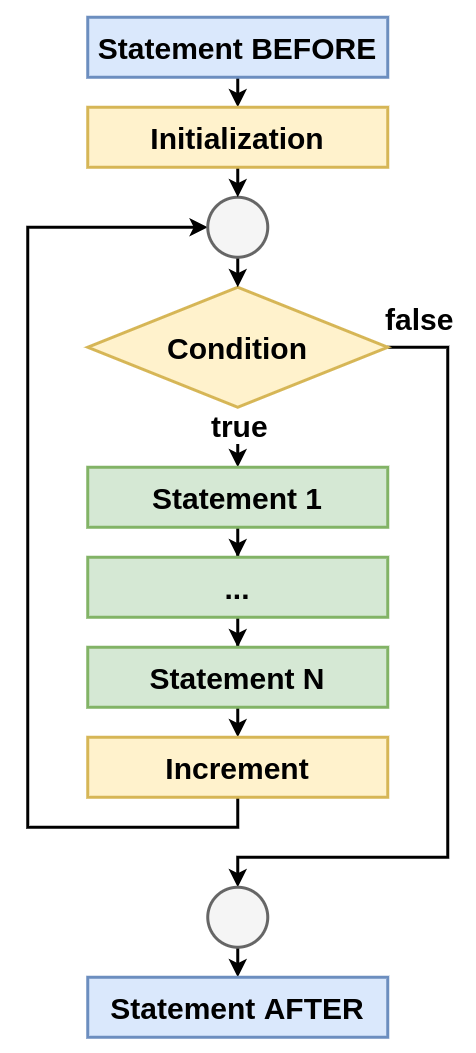
...for statement
Block schema
Syntax
for (initialization; termination; increment) {
// statement(s) (body of loop)
}Syntax
for (initialization; termination; increment)
// ONE statementDo not recommend
Concepts
for (initialization; termination; increment) {
// statement(s) (body of loop)
}The initialization expression initializes the loop; it’s executed ONCE, as the loop begins.
When the termination expression evaluates to false, the loop terminates.
The increment expression is invoked after EACH iteration through the loop
Example
int n = 5;
// for loop
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}1
2
3
4
5How this program works?
| Iteration | Variable | i <= n | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
1st |
|
|
|
2nd |
|
|
|
3rd |
|
|
|
4th |
|
|
|
5th |
|
|
|
6th |
|
| The loop is terminated. |
Example
int sum = 0;
int n = 1000;
// for loop
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// body inside for loop
sum += i; // sum = sum + i
}
System.out.println("Sum = " + sum);Sum = 500500Example
int sum = 0;
int n = 1000;
// for loop
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--) {
// body inside for loop
sum += i; // sum = sum + i
}
System.out.println("Sum = " + sum);Sum = 500500Example
// infinity for loop
for ( ; ; ) {
...
}Example
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i--) {
System.out.println("Hello");
}Hello
...for-each loop
Syntax
T[] array = initArray();
// for-each loop
for (T element : array) {
// statement(s)
}T - data type for elements from Array/Collection
Syntax
// for-each loop
for (T element : array)
// ONE statementT - data type for elements from Array/Collection
Example
// create an array
int[] numbers = {3, 9, 5, -5};
// for-each loop
for (int number: numbers) {
System.out.println(number);
}3
9
5
-5How to this program works?
In the first iteration, item will be
3.In the second iteration, item will be
9.In the third iteration, item will be
5.In the fourth iteration, item will be
-5.
for vs for-each
Example
char[] vowels = {'a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u'};// iterating through an array using a for loop
for (int i = 0; i < vowels.length; ++ i) {
System.out.println(vowels[i]);
}// iterating through an array using the for-each loop
for (char item: vowels) {
System.out.println(item);
}a
e
i
o
uTotal
Total
whilestatementкогда количество итераций зависит от результата вычисления в теле цикла
do-whilestatementкогда количество итераций зависит от результата вычисления в теле цикла, НО нужно выполнить как минимум одну итерацию
Total
forstatementкогда количество итераций заранее известно или легко вычисляется
for-each statement
при работе с каждым элементом Collection или Array