import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
public class MyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Socket s = new Socket("localhost", 6666);
DataOutputStream dout = new DataOutputStream(s.getOutputStream());
dout.writeUTF("Hello Server");
dout.flush();
dout.close();
s.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}Networking
Network models
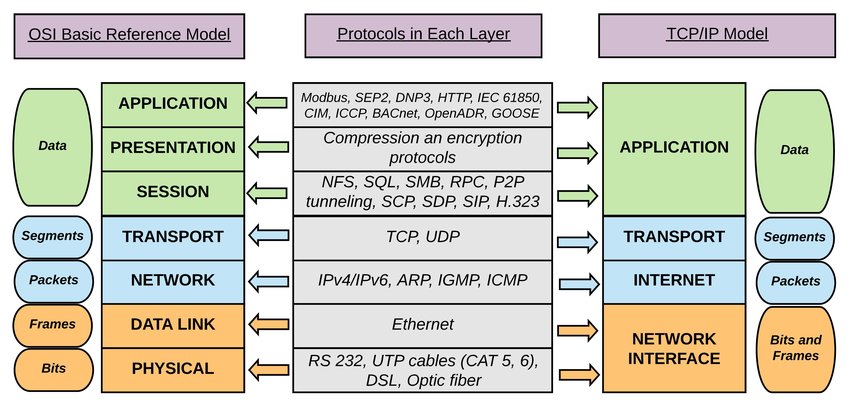
OSI vs. TCP/IP

OSI vs. TCP/IP
InetAddress
Methods
InetAddress getLocalHost()InetAddress getByName(String host)InetAddress[] getAllByName(String host)byte[] getAddress()String toString()String getHostName()boolean equals(Object obj)
TCP Networking
TCP Networking
SocketServerSocket
Socket: constructors
Socket()Socket(String host, int port)Socket(InetAddress address, int port)
Socket: methods
InputStream getInputStream()OutputStream getOutputStream()void close()void setSoTimeout(int timeout) throws SocketException
Example
ServerSocket: constructors
ServerSocket() throws IOExceptionServerSocket(int port) throws IOExceptionServerSocket(int port, int backlog) throws IOExceptionServerSocket(int port, int backlog, InetAddress bindAddr) throws IOException
ServerSocket: methods
Socket accept()void bind(SocketAddress endpoint)void close()ServerSocketChannel getChannel()InetAddress getInetAddress()
ServerSocket: methods
int getLocalPort()SocketAddress getLocalSocketAddress()int getReceiveBufferSize()boolean isClosed()void setReceiveBufferSize(int size)
Example
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(6666);
Socket s = ss.accept();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(s.getInputStream());
String str = (String) dis.readUTF();
System.out.println("message= " + str);
ss.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}UDP Networking
DatagramSocket: constructors
DatagramSocket() throws SocketExeptionDatagramSocket(int port) throws SocketExeptionDatagramSocket(int port, InetAddress address) throws SocketExeption
DatagramPocket: constructors
DatagramPacket(byte [] barr, int length)DatagramPacket(byte [] barr, int length, адрес InetAddress, int port)
Example: Sender
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
public class Sender {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket();
String str = "Welcome java";
InetAddress ip = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(str.getBytes(), str.length(), ip, 3000);
ds.send(dp);
ds.close();
}
}Example: Receiver
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
public class Receiver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(3000);
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf, 1024);
ds.receive(dp);
String str = new String(dp.getData(), 0, dp.getLength());
System.out.println(str);
ds.close();
}
}