public class EmailSender {
void send(Message message) {
try {
Transport.send(message);
} catch (MessagingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Intro to Spring
Intro to Spring

Simplifying Java development
Простая разработка с POJOs (Plain Old Java Objects)
Слабая связь через dependency injection и ориентация на интерфейсное взаимодействие
Упрощенная конфигурация приложения
Сокращение объема программного кода через аспекты и шаблоны
Декларативная разработка через применение аспектов и общих соглашений
Возможность управления общими зависимостями в единственном репозитории
About Spring
Actual version (Spring Framework): 5.2.8 (21.07.2020)
Site and Docs: https://spring.io/
Spring Projects
Spring Projects
Spring Boot
Spring Framework
Spring Data
Spring Cloud
Spring Cloud Data Flow
Spring Security
Spring Session
Spring Integration
Spring Projects
Spring HATEOAS
Spring REST Docs
Spring Batch
Spring AMQP
Spring for Android
Spring CredHub
Spring Flo
Spring for Apache Kafka
Spring Projects
Spring LDAP
Spring Mobile
Spring Roo
Spring Shell
Spring Statemachine
Spring Vault
Spring Web Flow
Spring Web Services
OMG
What to use from these projects?
Spring Framework
Spring Data
Spring Security
Spring Boot
Spring Framework
Overview
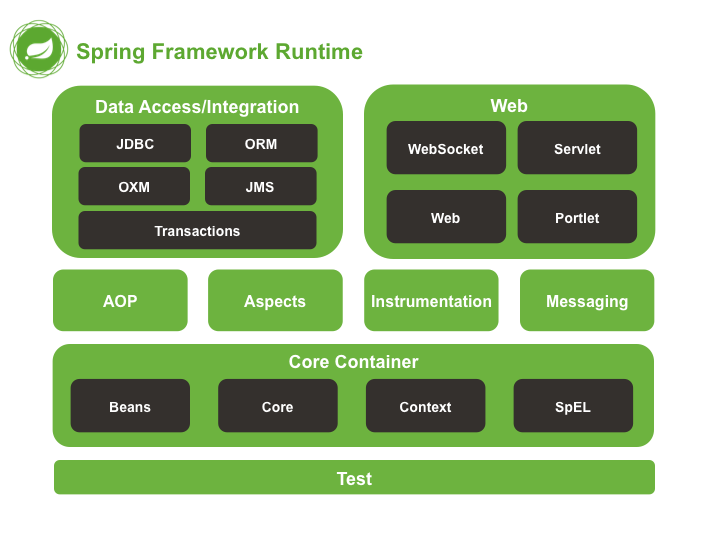
Spring Framework Artifacts
GroupId | ArtifactId | Description |
|
| Proxy-based AOP support |
|
| AspectJ based aspects |
|
| Beans support, including Groovy |
|
| Application context runtime, including scheduling and remoting abstractions |
|
| Support classes for integrating common third-party libraries into a Spring application context |
|
| Core utilities, used by many other Spring modules |
|
| Spring Expression Language (SpEL) |
Spring Framework Artifacts
GroupId | ArtifactId | Description |
|
| Instrumentation agent for JVM bootstrapping |
|
| Instrumentation agent for Tomcat |
|
| JDBC support package, including DataSource setup and JDBC access support |
|
| JMS support package, including helper classes to send/receive JMS messages |
|
| Support for messaging architectures and protocols |
|
| Object/Relational Mapping, including JPA and Hibernate support |
|
| Object/XML Mapping |
Spring Framework Artifacts
GroupId | ArtifactId | Description |
|
| Support for unit testing and integration testing Spring components |
|
| Transaction infrastructure, including DAO support and JCA integration |
|
| Foundational web support, including web client and web-based remoting |
|
| HTTP-based Model-View-Controller and REST endpoints for Servlet stacks |
|
| WebSocket and SockJS infrastructure, including STOMP messaging support |
Core Container
Core Container

Core Container modules
spring-core- provides the fundamental parts of the framework, including the IoC and Dependency Injection featuresspring-beans- providesBeanFactory, which is a sophisticated implementation of the factory patternspring-context- builds on the solid base provided by thespring-coreandspring-beans, and it is a medium to access any objects defined and configured. TheApplicationContextinterface is the focal pointspring-context-supportspring-expression- provides a powerful expression language for querying and manipulating an object graph at runtime
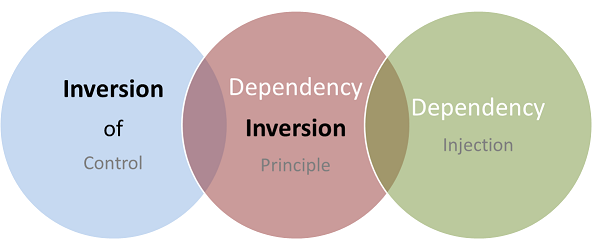
IoC, DIP and DI
Problem
Solution
Inversion of Control
Dependency Inversion Principle
Dependency Injection
Problem: strong coupling
Problem: strong coupling
public class SenderService {
private EmailSender sender;
public SenderService() {
}
public SenderService(EmailSender sender) {
this.sender = sender;
}
public void sendMessage(Message message) {
sender.send(message);
}
public void setSender(EmailSender message) {
this.sender = sender;
}
}Solution: weak coupling
public interface Sender {
void send(Message message);
}Solution: weak coupling
public class EmailSender implements Sender {
void send(Message message) {
try {
Transport.send(message);
} catch (MessagingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Solution: weak coupling
public class SenderService {
private Sender sender;
public SenderService() {
}
public SenderService(Sender sender) {
this.sender = sender;
}
public void sendMessage(Message message) {
sender.send(message);
}
public void setSender(Sender message) {
this.sender = sender;
}
}Benefit
SenderServiceне привязан к конкретной реализацииSenderSenderServiceневажно какой вид адреса передается в конструктор, т.к. передаются классы-потомкиSenderweak coupling - объект знает о связи по интерфейсу, таким образом зависимость может быть вынесена с различными реализациями, без информации о конкретной реализации
IoC Container
IoC - Inversion of Control, инверсия управления
Принцип объектно-ориентированного управления, который используется для уменьшения зацепления в программе.
Упрощает расширение возможностей системы
IoC Container
Dependency Injection
Подход в проектировании, при котором зависимости объекта передаются ему извне, а не создаются в нём
Упрощает тестирование системы
Позволяет настраивать процесс создания объектов извне
Dependency Injection
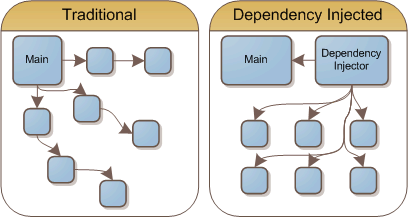
Bean
Объект в терминах IoC-контейнера, жизненный цикл которого управляется этим контейнером
Может представлять собой любой объект:
service
dao
util (вспомогательный класс)
т.д.
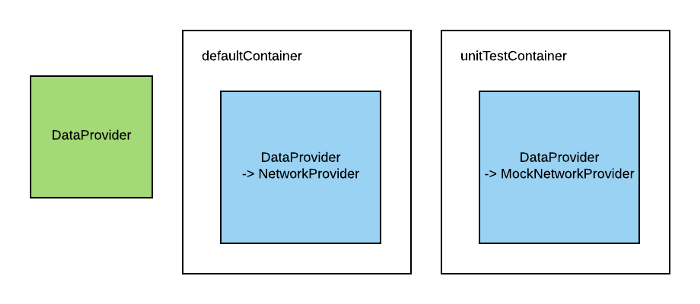
Example
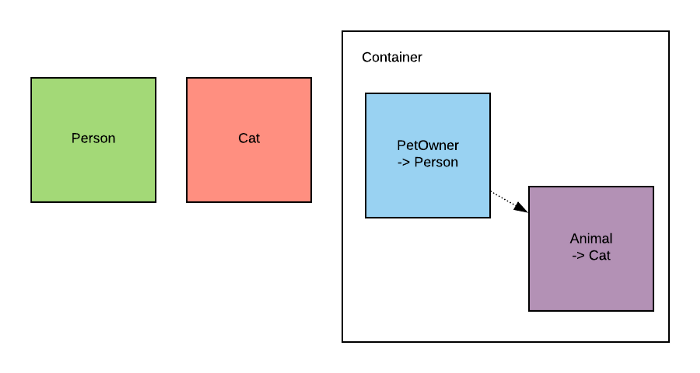
Example
Bean Definition
Описание правил, по которым создаётся бин, а также его зависимостей и правил их внедрения
Может задаваться различными способами:
xml
java-config
annotations
groovy-config
IoC Container
IoC Container
Spring provides following two types of containers:
BeanFactorycontainerApplicationContextcontainer
BeanFactory
public class Program {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("beans.xml");
BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(is);
//Get bean
HelloWorld obj = (HelloWorld) factory.getBean("helloWorld");
}
}BeanFactory
public class Program {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Resource resource = new FileSystemResource("beans.xml");
BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(resource);
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource("beans.xml");
BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(resource);
}
}BeanFactory methods
boolean containsBean(String)Object getBean(String)Object getBean(String, Class)Class getType(String name)boolean isSingleton(String)String[] getAliases(String)
ApplicationContext
Фактически
ApplicationContext- является IoC Container, в котором хранятся все beansПредставляет собой
HashMap
Виды ApplicationContext
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext- считывает определения beans из xml-файла, расположенного где-то в файловой системеClassPathXmlApplicationContext- считывает определения beans из xml-файла, расположенного в classpathAnnotationConfigApplicationContext- считывает определения beans из конфигурационных Java-файлов
Виды ApplicationContext
XmlWebApplicationContext- считывает определения beans из xml-файла в web-приложенииAnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext- считывает определения beans из конфигурационных Java-файлов в web-приложенииGenericGroovyApplicationContext(Spring 4+) - считывает определения beans из конфигурационных Groovy-файлов
How create?
Add dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>Bean Definition
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="quest" class="by.rakovets.course.spring.example.bean.knights.SlayDragonQuest">
<property name="steps">
<list>
<value type="java.lang.String">Find dragon lair</value>
<value type="java.lang.String">Create trap</value>
<value type="java.lang.String">Slay dragon</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean class="by.rakovets.course.spring.example.bean.knights.BraveKnight">
<constructor-arg name="quest" ref="quest"/>
<property name="name" value="Fedor"/>
</bean>
</beans>Use with ApplicationContext
public class XmlFileConfigApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context
= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application-context.xml");
Knight knight = context.getBean(BraveKnight.class);
knight.embarkOnQuest();
}
}Spring namespaces
Spring namespaces
aop– предоставляют элементы для декларирования аспектов, и для автоматического проксирования@AspectJ– аннотированные классы как Spring аспекты.beans– базовые примитивы Spring namespace, включая декларирование beans и как они должны быть связаны.context– приходят с элементами для конфигурирования Spring контекст приложения, включая возможность для автоопределения и autowired beans и введения объектов не прямо управляемых Spring.
Spring namespaces
jee– предлагает интеграцию с Jakarta EE API таких, как JNDI и EJBjms– предоставляет конфигурационные элементы для декларирования message-driven POJOslang– включает декларирование beans, которые реализованы на Groovy, JRuby или BeanShell скриптов.
Spring namespaces
mvc– включает Spring MVC возможности, такие как annotation-based (аннотационно-ориентированных) controllers, view-controllers, и interceptors.oxm– поддержка конфигурации Spring object-to-XML маппинг возможности.tx– предоставляет декларативные транзакционные конфигурации.